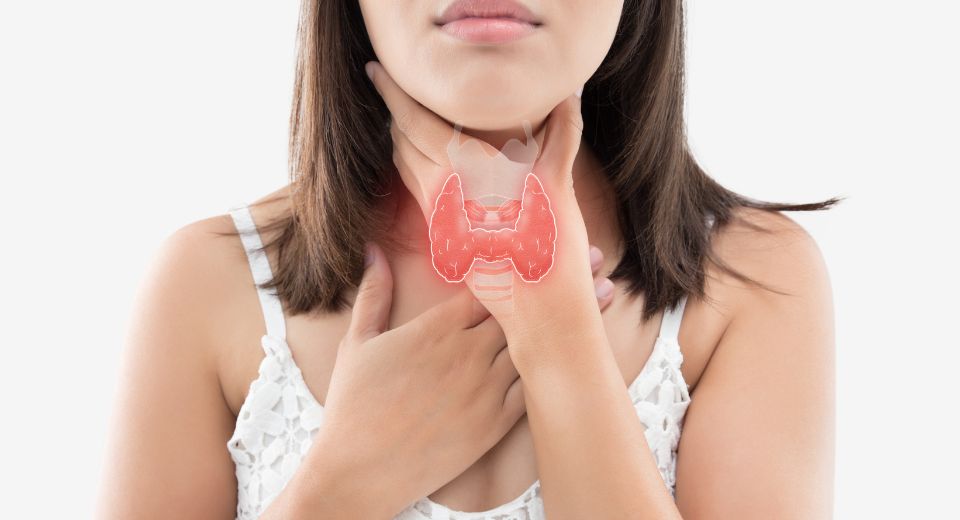
The thyroid, a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into what the thyroid is, its functions, common thyroid diseases, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Additionally, we’ll highlight the significance of January as Thyroid Awareness Month.
The Thyroid Gland and Its Functions
Situated in the front of the neck just below the Adam’s apple, is a crucial component of the endocrine system. Its primary function is to produce hormones—thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)—that regulate various metabolic processes in the body. These hormones influence energy production, metabolism, and the functioning of organs and tissues.
Types of Thyroid Diseases
- Hypothyroidism: This condition occurs when the gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. Common causes include autoimmune disorders (like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), iodine deficiency, and certain medications.
- Hyperthyroidism: Characterized by an overproduction of thyroid hormones, hyperthyroidism can be caused by conditions such as Graves’ disease or nodules on the thyroid.
- Nodules: These are abnormal growths on the thyroid gland, which may be benign or, in some cases, cancerous.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid, often caused by autoimmune disorders or viral infections.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
– Hypothyroidism: Fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, and depression.
– Hyperthyroidism: Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, excessive sweating, and irritability.
– Nodules: Swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or changes in voice.
– Thyroiditis: Neck pain, swelling, and sometimes fever.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing thyroid disorders involves a combination of blood tests measuring hormone levels, imaging studies like ultrasound, and, if necessary, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy to assess nodules for cancerous cells.
Prevention and Treatment
- Iodine Intake: Ensure sufficient iodine intake through diet or supplements to prevent iodine deficiency-related disorders.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine function tests can help detect and manage disorders early.
- Medication: Hormone replacement therapy is common for hypothyroidism, while anti-thyroid medications or radioactive iodine may be prescribed for hyperthyroidism.
- Surgery: In cases of nodules or cancer, surgical removal of part or all may be recommended.
January is Thyroid Awareness Month
It aims to raise awareness about thyroid disorders and the importance of early detection and treatment. During this month, healthcare organizations and advocacy groups conduct campaigns to educate the public about thyroid health, symptoms, and the significance of regular check-ups.
Understanding its impact on overall health is crucial for maintaining a balanced and thriving life. By being aware of its disorders, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to prioritize their health. As we enter Thyroid Awareness Month, let us promote awareness, education, and advocacy to ensure optimal well-being for everyone.
Author: David Porzio, MD
The information provided is for general interest only and should not be misconstrued as a diagnosis, prognosis or treatment recommendation. This information does not in any way constitute the practice of medicine, or any other health care profession. Readers are directed to consult their health care provider regarding their specific health situation. Marque Medical is not liable for any action taken by a reader based upon this information.

Favorite Platform

New Content